
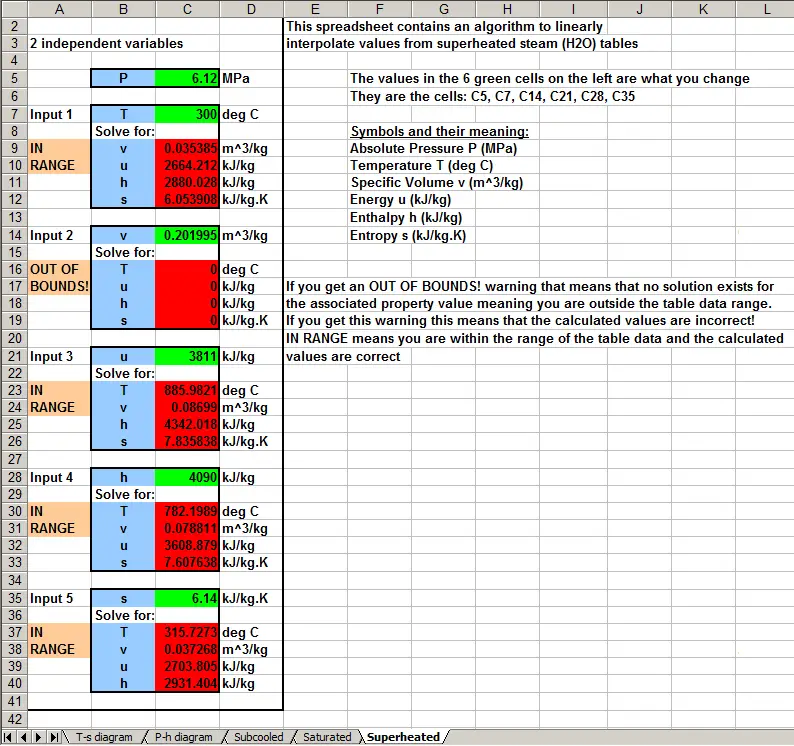
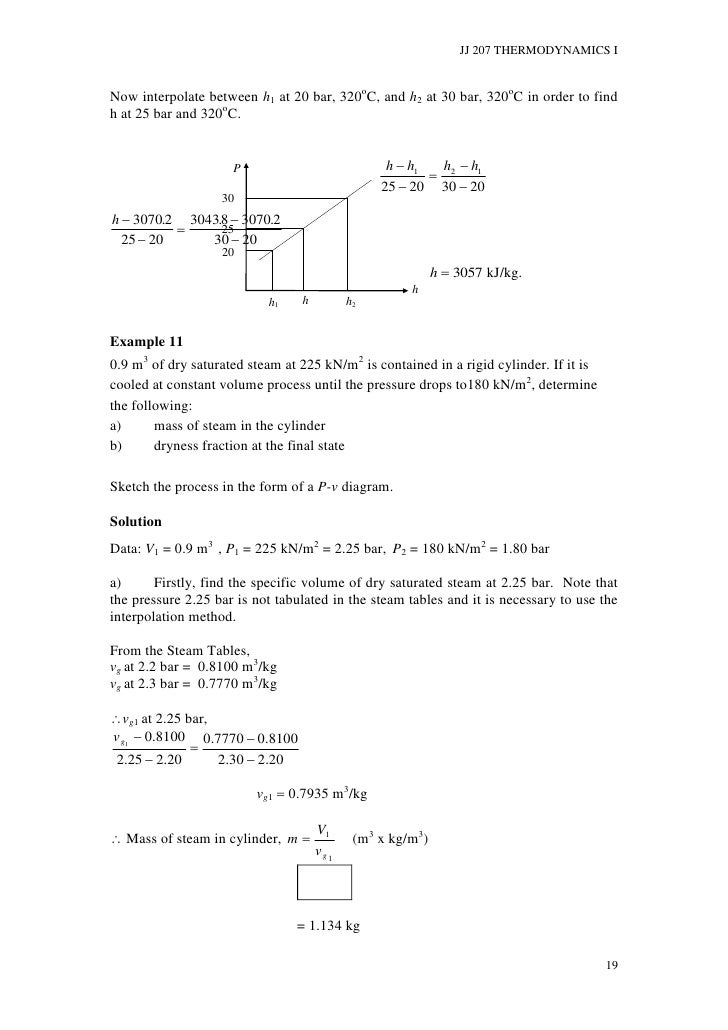
Given that friction is unavoidably present, explain why this ride is an example of an irreversible process. As the riders descend down the ride, the "falling" energy is used to recharge the battery. To make the ride as energy efficient as possible, one can set up an electric motor and regenerative battery system in which energy from the battery is used to drive the electric motor to lift the riders to the top of the ride. Using online resources, analyze the efficiency of the Air Car.Ī Drop Tower is a popular ride in amusement parks. The volume of the tank is 0.3 m 3, and the initial temperature and pressure of air inside the tank is 20☌ and 30 MPa, respectively. The pressurized tank is connected to an air-powered engine.
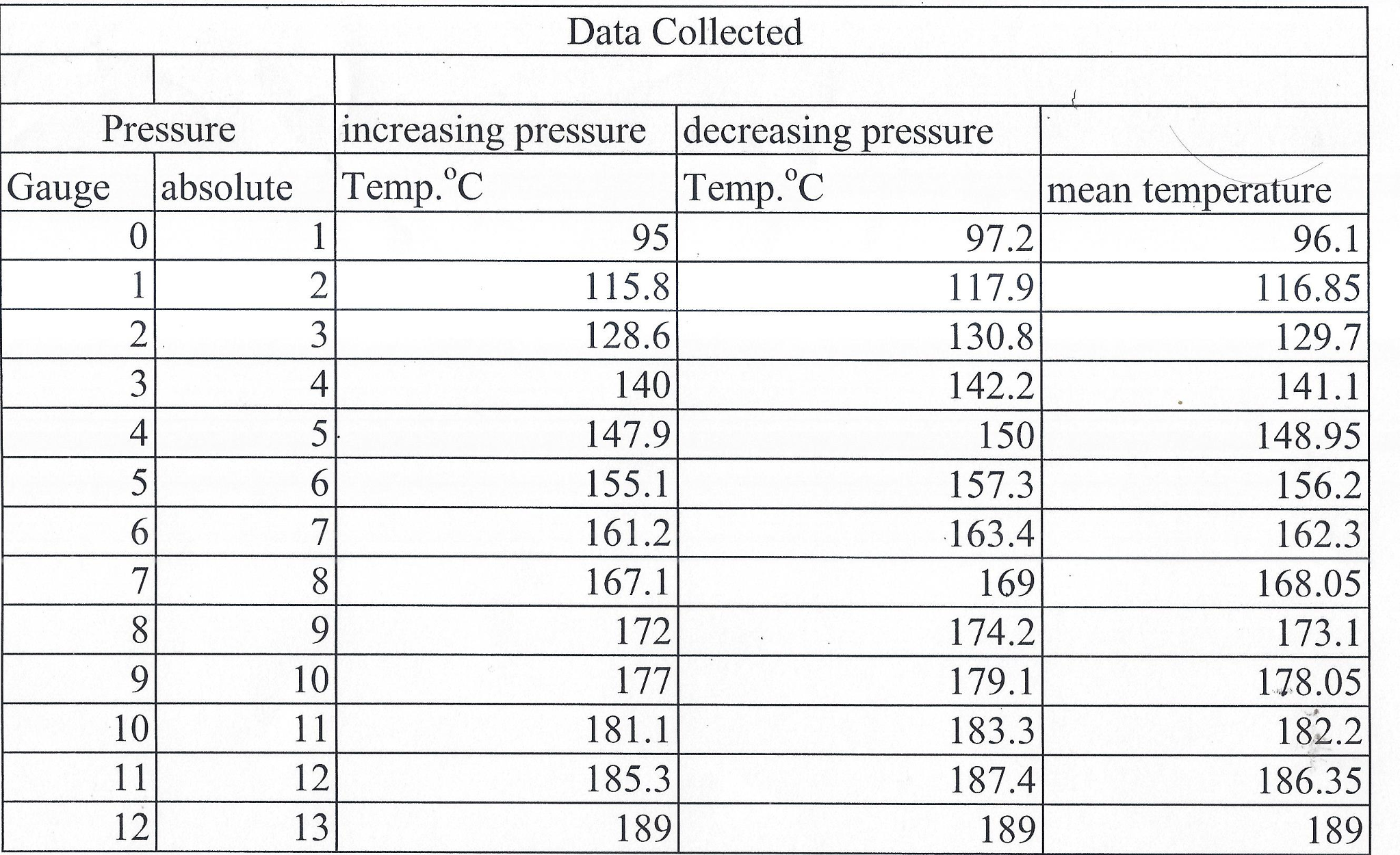
Are these specifications possible?Īn air-powered car is powered using high pressure compressed air stored in a tank. The ratio of mass flow rate between the cold stream and the inlet stream is 0.70. Hot air exits the right side of the tube at a temperature of 105☌ and at atmospheric pressure. Cold air exits the left side of the tube at a temperature of -18☌ and at atmospheric pressure. According to a manufacturer's specifications, pressurized air enters a vortex tube at a temperature of 20☌ and a guage pressure of 700 kPa. What is the enthalpy of the steam?Ī vortex tube, also known as a Ranque-Hilsch vortex tube, is a mechanical device without moving parts that separates a compressed gas into hot and cold streams. Steam at a temperature of 350☌ and a pressure of 1 MPa is flowing through a pipe. Using the equation above, why would this produce more power output than using non-concentrated solar energy as the heat source, collected over the same area as the dish. In an application involving a Stirling engine (a type of heat engine, shown below), a parabolic dish is used to concentrate solar energy onto the receiver of the engine. The term inside the brackets represents the thermal efficiency of the process, commonly known as the Carnot efficiency. Both temperatures are in units of Kelvin. Where T H is the temperature of the heat source, and T L is the temperature of the heat sink, which is the temperature of the "leftover" heat energy after work is extracted from the process. What is the maximum pressure inside the container so that water does not condense on the inside of the container? Assume the air temperature inside the container is 20☌.įor all heat engines, the maximum work output ( W) is related to the maximum heat input energy ( Q) by the following equation: Explain why the process described is not reversible.Īir with a relative humidity of 30% at 20☌ is pumped into a container.
This means that the process can happen in the reverse direction. In thermodynamics, a process is said to be reversible if it produces no entropy. After the gas has settled, the final conditions of the gas are P 2, V 2, m, and T 2. A valve is then opened which allows the gas to expand freely into an insulated container B, which is initially empty. These quantities represent pressure, volume, mass, and temperature, respectively. This is why I chose problems which have at least some practical relevance.Ī gas is initially contained inside an insulated container A, at initial conditions P 1, V 1, m, and T 1. Thermodynamics is somewhat of a strange subject which isn't always easy to connect to the real-world in the way that, say, dynamics theory is. These problems are designed to help you understand some of the fundamentals without going into too much depth. On this page I put together a collection of thermodynamics problems to help you understand thermodynamics better.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
